Djibouti is one of the smallest states in Africaand trapped between Eritrea, Ethiopia and Somalia – countries that are regularly at war. Unlike its neighbors, Djibouti is a fairly stable country, but it is too often ofTraveleris only used as a transit country. The country offers tourists unique landscapes full of extremes (e.g. the Danakil Desert one of the hottest and deepest regions in the world), lakes full of flamingos and fantastic diving areas on the Red Sea. In the north of Djibouti there are volcanic mountains that rise to over 2,000 m.
The Peoplein Djibouti are rather poor. The unemployment rate is currently over 60 percent. More and more people are migrating from the countryside to the cities. As a result, unemployment continues to rise there. People who have moved in hope to find work in the city, but in most cases they are bitterly disappointed.
The country of Djibouti is said to be underdeveloped. This becomes clear when you know that over half of the urban population has to live in slums. Most of the residents of Djibouti are Somali. They make up more than 60 percent of the total population. The south is populated with Afar, which still make up about 20 percent of the total population.
A major problem is that it doesn’t rain enough in Djibouti. This complicates the cultivation of exportable food. The region is characterized by thorn bush savannah, semi and full desert. In the Foret du Day nature park, a forest area is protected that would otherwise have disappeared. When visiting the country of Djibouti, you should definitely visit this park. There you can discover the original beauty of Djibouti’s nature.
Some gazelles, antelopes and zebras live in the dry areas of the country. Hyenas and jackals obviously also feel comfortable there. The Lake Abbe is in the south of Djibouti and is a true paradise for ibis, pelicans and flamingos. You are immediately impressed by the sight.
Area: 23,000 km² (land: 22,980 km², water: 20 km²). Djibouti is one of the smallest countries in Africa.
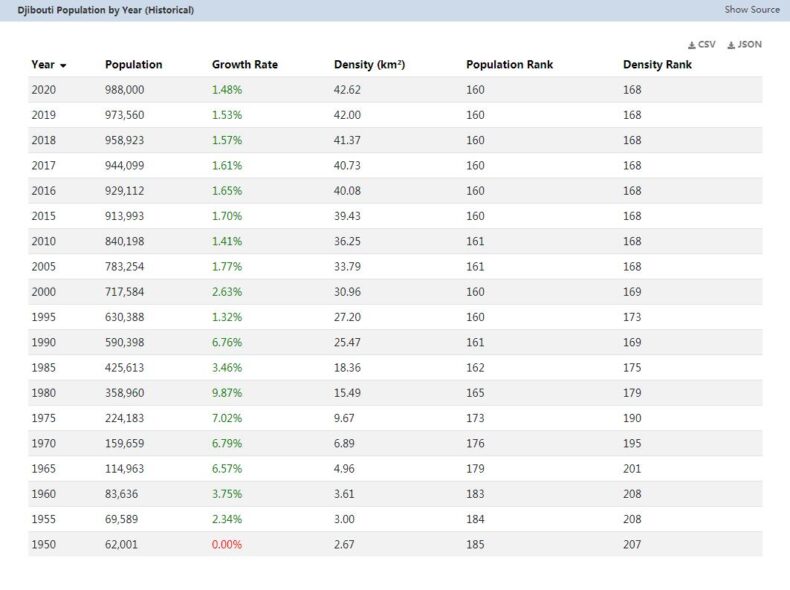
Population: 757,074 people (July 2011, COUNTRYAAH.COM). Djibouti is the country with the smallest population on the African mainland. The population is made up of two hamatic groups: the Somalis or Issas with 62% who live in the south and the Afar, about 20% who live in the northern and western regions of the country. Minorities of Yemenis and Europeans also live in the country.
Density: 33 people per sq. Km
Population growth: 2.237% per year (2010, CIA)
Capital: Djibouti (about 360,000 residents).
Here is a detailed summary of the largest cities in Djibouti.
Highest point: Moussa Ali, 2,063 m
Lowest point: Lac Assal -155 m, also the lowest point in Africa
Form of government: Djibouti has been a presidential republic since 1977. The constitution dates from 1992. The National Assembly (Assemblée Nationale) consists of 65 deputies (33 Issa, 32 Afar) who are elected every five years. Djibouti has been independent of France since June 27, 1977.
Administrative division: 6 districts (French cercles, singular – cercle): Ali Sabieh, Arta, Dikhil, Djibouti, Obock and Tadjoura
Prime Minister: Abdoulkader Kamil Mohamed, since April 1, 2013
Head of state: President Ismail Omar Guelleh, since May 8, 1999
Language: Official languages are Djibouti Arabic and French. In addition, Cushitic languages such as Somali and Afar are spoken. English is only spoken in upscale hotels in Djibouti, even in the capital. Without knowledge of French, a trip to Djibouti is complicated. If necessary, you can rely on interpreters that any better hotel can provide.
Religion: 94% Muslims (Sunnis), as well as smaller Roman Catholic, Protestant and Greek Orthodox minorities
Local time: CET + 2 h. In Djibouti there is no change between summer and winter time. The time difference to Central Europe is + 2 h in winter and +1 h in summer
Telephone code: 00253 or +253
Internet identifier:.dj
Mains voltage: 220 V, 50 Hz
Geography
Djibouti is located on the Strait of Bab el Mandeb on the “Horn of Africa” and borders in the southeast on Somalia, in the west and south on Ethiopia, in the northwest on Eritrea and in the east on the Gulf of Aden. Djibout is located on a relatively barren stretch of coast that is between 20 and 90 km wide. The coast mainly consists of sandy beaches. A mountain range adjoins the coastal plain and reaches heights of up to around 1,000 m. These mountains change into a plateau, which is mainly covered by semi-desert.
Here you can find a detailed topographic map of Djibouti.
The highest point of Djibouti is on the border with Ethiopia and Eritrea in the Mouso Ali with 2,063 m.
Djibouti is strongly volcanic, and tectonic activities are still taking place today due to the lifting of the East African shield and the emergence of the East African trench system. For example, the Ardoukoba volcano was only created in 1978.
The southern part of the country is dominated by plains and basalt ceilings. Here the water of the wadis, which only flows in temporarily, evaporates in drainless sinks and salt pans. Some of the salt deposits created in this way are mined by the Afar.
The Assalsee in this region is the lowest point of Africa with -155 m. Worldwide only the Dead Sea is lower in Israel / Jordan.
Population in Djibouti
This map of the population distribution in Djibouti was created by the Worldmapper team. Densely populated areas appear bloated, the area of sparsely populated areas is reduced. The shape of the grid has been preserved; an underlying map with the original geographical extent helps interpret the map. The distorted map should help to present abstract statistical information clearly.